STAINS AND DYES
Stains and dyes are used to great lengths in microbiology to highlight certain parts or organelles of cells when put under the microscope. They can also be used to classify the various parts of the cells and different cell groups in a tissue. Stains can be used on their own as well as mixed with other stains and dyes. In fact, the process of using multiple stains to highlight important parts of an already stained cell is called counterstaining. You may have used safranine while preparing a temporary mount of leaf peel to observe stomata. That is an example of a stain.
When it comes to the process of applying stains, there are broadly two different classifications: IN VIVO staining and IN VITRO staining. As the name suggests, IN VIVO staining is practised on live tissue. It helps us observe the chemical reactions taking place within a living cell. Stains are used here to highlight the chemicals and chemical reactions taking place.
IN VITRO staining is practised on cells and tissues removed from their biological context. Staining here is usually not single i.e usually multiple stains are applied so that scientists can observe the various parts of the fixed sample. Many cells in a tissue may continue to perform some life processes until they are “fixed”. Different stains can be applied to the living and non-living parts of the cell. The stains that apply to the non-living parts of a cell are known as “vital stains”. These include stains like propidium iodide and erythrosine. These, quite ironically, get rejected by the living cells and apply to the dead cells.
Supravital stains, on the other hand, apply to the living cells in a tissue. They get accepted by the living cells but are toxic for the organism being studied and the living soon become the dead cells. These include stains like Nile blue, Methyl violet and Hoechst stain. As one can notice, stains are often named after the colour they represent.
Here let us take the example of two common stains: Iodine and Safranine.
Iodine
Iodine is not only the 53rd element of the modern periodic table, it is also a stain! Lugol’s iodine (IKI) is used as a stain in the test for starch. It is brown in colour in its aqueous solution, but turns black in the presence of starch. It can also be used as a cell stain for the nuclei of the cell, making it more visible.
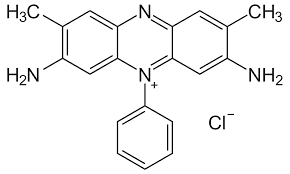
Safranine
Safranine (C20H19ClN4) is a compound used for the staining of cell nuclei red while counterstaining. It is often confused with ‘saffron’, an expensive dye which also happens to appear in the Indian flag (Jai Hind!). It is also misspelled as ‘safranin’ but it requires the –ine ending as it is an amine.
Stains and dyes are also used in woodwork, where they are used to add colour to wood. There we can notice a difference between stains and dyes. Stain contain pigments for adding colour along with binders to help bind to the wood. Binders are glue-like substances which help the pigment get stuck to the wood.
Dyes, however do not contain pigments or binders but are clear and practically transparent so that the wood underneath can be seen. Dyes can be applied when they are mixed with water and alcohol which are not binders. They also sink into the wood so that the dyed wood feels the same as the wood you obtain from trees.
This article is written by Aman Thukral of Amity International School!!!
Enjoy your high school with - High School Pedia : www.highschoolpedia.com
Enjoy your high school with - High School Pedia : www.highschoolpedia.com
Comments
Post a Comment